Spring Framework :
Facts:Spring Framework is a lightweight framework.Do you know reason.Read out
Proof: As Spring follow MVC model as following
Does the image show that spring framework is light weight framework.If you are new then you might be confuse.So Don't be confuse go to the below coding example which proves it's light weight properties.
Reason.1-> Use Of POJO's
POJO means Plain Old Java Object. It refers to a Java object (instance of definition) that isn't bogged down by framework extensions. For example, to receive messages from JMS, you need to write a class that implements the MessageListener interface.
Coming to a simple example.
Here College class has it's own property name & Address.It include references s1 for student type class & similarly t1 for Teacher type class.As there is a case of Assciation(HAS-A) relationship between college and student.Similarly to teacher also.But if you analyze this College Pojo class you will find that this object model try to solve the lots ofcomplexity .Before the spring if you want to do the samething then you need to do as below.
This make the spring lightweight as you can see.
Reason.2-> Use of IOC.
Before IOC if you want to configure your datasource connection you need to write lengthy code.
Properties of Database
Drivermanger aquire the connection
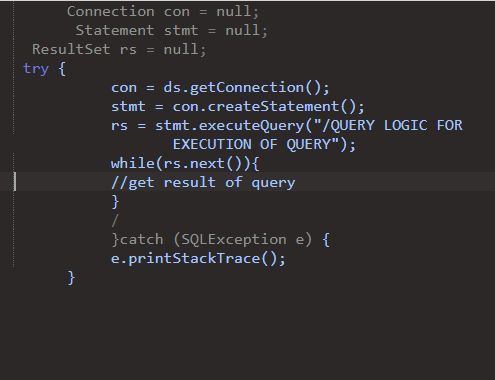
These above lines are called at Dao layer at every time when you want to execute your db query.Can you imagine how much weight could JVM handle for this purpose.Each time JVM cry .
After Spring IOC it turn the number of lines code to
And simply use your datasource configuration where you need to get connect.
Thanks for Reading. Please comments.







Comments
Post a Comment